Dec 31, 2025
In automation systems, flame retardant tubing is rarely the most visible component, yet it often becomes critical when safety audits, certifications, or unexpected failures occur. Many users assume that “flame retardant tubing” means it will not burn at all, but in reality, flame retardant ≠ non-combustible. Just like a waterproof device cannot be thrown into deep water without limits, flame retardant tubing is designed to control fire behavior, not eliminate it. Understanding how to distinguish flame retardant grades—especially under the UL94 standard—is essential for distributors, engineers, and purchasing teams alike.
When customers search for flame retardant polyethylene tubing or flame resistant tubing , they often expect a single clear definition. In practice, flame retardancy is a measured performance, not a marketing label. A tubing material is evaluated based on how quickly it extinguishes itself after ignition, whether molten droplets fall, and whether those droplets can ignite other materials. These criteria directly affect system safety in control cabinets, robotic cells, and automated production lines where compressed air and electrical components coexist.
From an engineering perspective, flame retardant tubing is primarily used to limit flame propagation, reduce secondary ignition risks, and give operators or systems valuable reaction time during abnormal events. This is why international standards such as UL94 exist—to turn vague safety claims into verifiable data.
The UL94 flammability standard, developed by Underwriters Laboratories, is widely accepted in North America and globally. It applies to plastic materials used in electrical and industrial products, including flame retardant tubing and pipe insulation.
UL94 evaluates materials under controlled laboratory conditions, measuring flame duration, afterglow time, and dripping behavior. For tubing used near solenoid valves, control panels, or actuators, this standard provides a common technical language between manufacturers, inspectors, and end users.
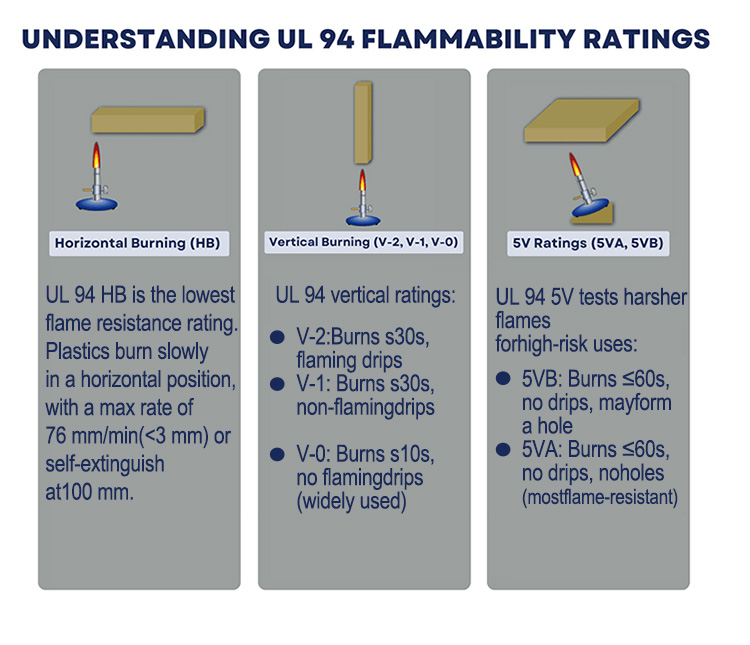
1.UL94 V-0 Flame Rating – The Commercial Benchmark
UL94 V-0 flame rating represents the highest flame retardant performance commonly used in commercial and industrial products. After two 10-second flame applications, the material must self-extinguish within 10 seconds, with no flaming drips allowed. This makes V-0 the preferred choice for applications where tubing runs close to electrical wiring or heat sources.
In many markets, UL94 V-0 is considered equivalent to GB/T 2408 V-0, which simplifies compliance for global equipment manufacturers exporting to different regions.
2.UL94 V-1 and V-2 – Controlled but Limited
V-1 materials allow a longer self-extinguishing time (up to 30 seconds) and still prohibit flaming drips. V-2 permits flaming drips, as long as they do not ignite cotton placed below the sample. These grades may be acceptable in low-risk pneumatic routing but are rarely recommended for enclosed electrical environments.
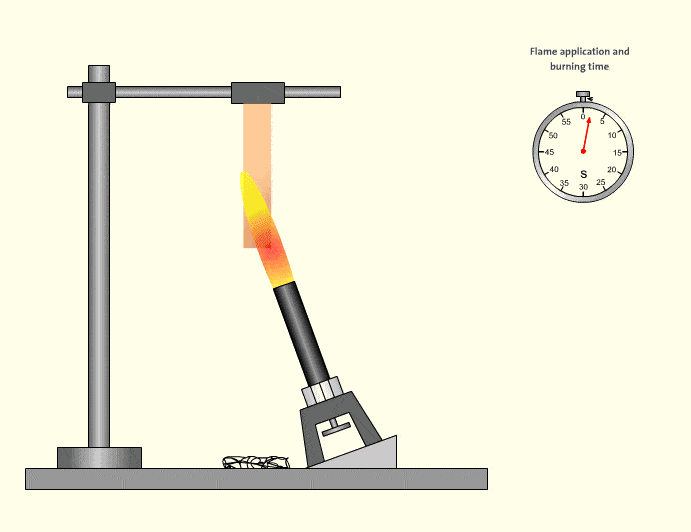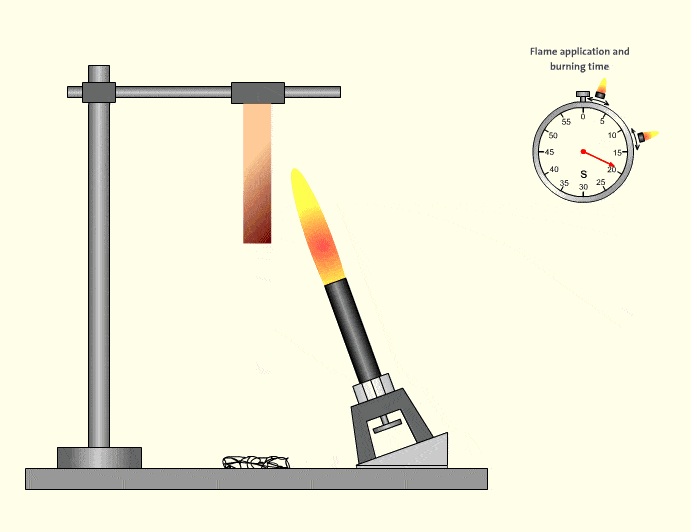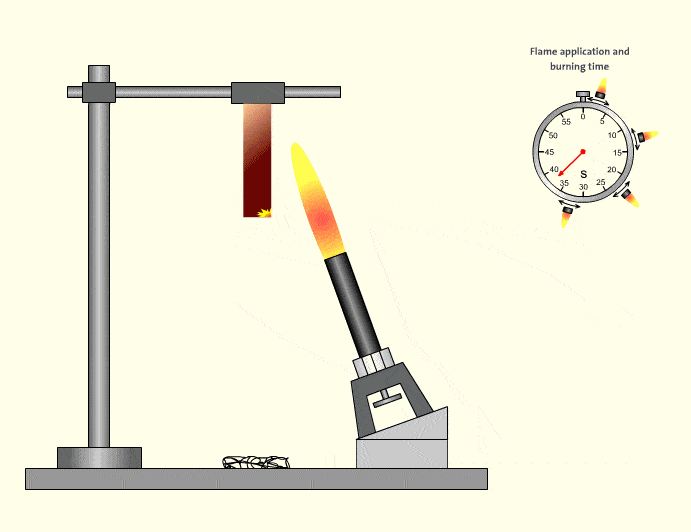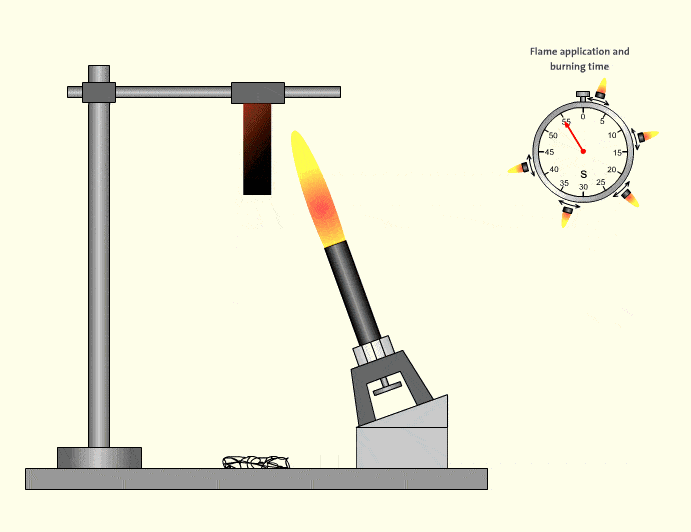
3.UL94 HB – Basic Horizontal Burning
HB is the lowest classification and does not qualify as flame retardant in many industrial interpretations. Materials may burn slowly but are not self-extinguishing in the same manner. HB-rated tubing is generally unsuitable for safety-critical automation systems.
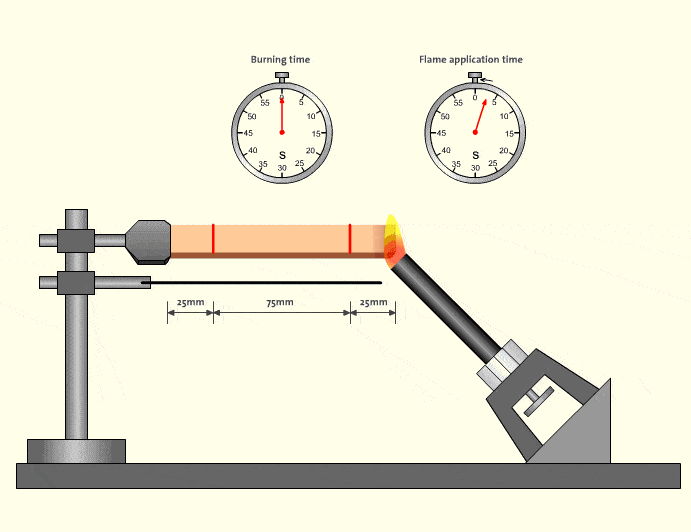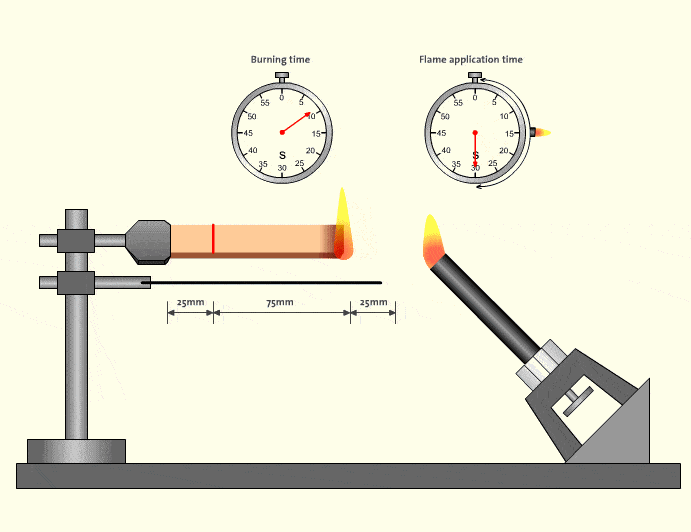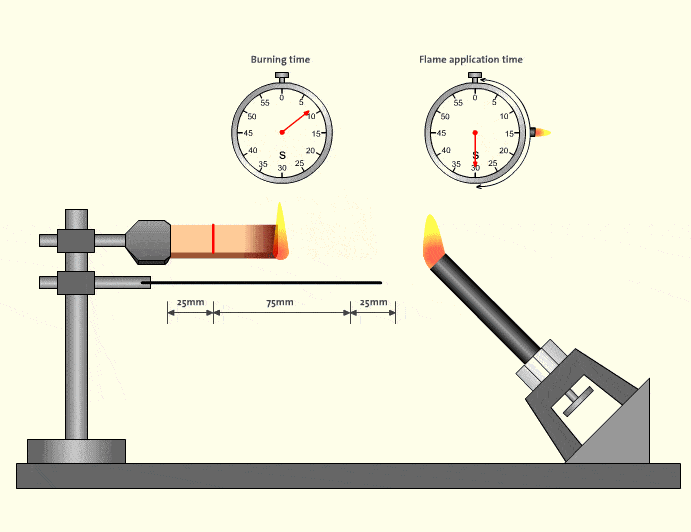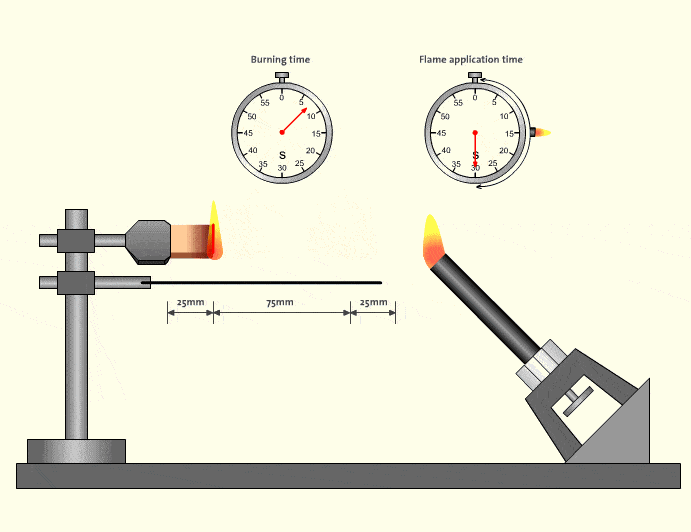
In real-world factory environments, flame events rarely happen in isolation. A small ignition source can quickly spread if tubing melts, drips, or continues burning. This is why V-0-rated flame retardant tubing has become a de facto requirement for equipment exported to North America and Europe.
Industry safety analyses consistently show that materials meeting V-0 significantly reduce secondary fire risks in control cabinets and robotic workstations (source type: industrial safety reports). For distributors and OEM customers, choosing V-0 is not only about compliance—it reduces liability and simplifies customer approvals.
Some engineers encounter the 5VA rating when reviewing the UL94 standard. While 5VA represents even stricter flame resistance, including resistance to burn-through, it is primarily applied to rigid housings rather than flexible tubing. Achieving 5VA performance in a flexible pneumatic tube would severely compromise elasticity and installation performance, making it impractical for most automation systems.
A common issue in the market is vague labeling such as “flame resistant tubing” without a clear test standard. For professional buyers and engineers, verification should always include:
◆A declared UL94 rating (e.g., UL94 V-0)
◆Test reports from recognized laboratories (UL, SGS, TÜV)
◆Clear identification of the tested material structure
Relying solely on supplier statements without documentation can expose distributors and end users to compliance risks during audits or export inspections.
FOKCA’s PUFR flame retardant tubing is designed specifically for automation environments requiring UL94 V-0 flame rating performance. The tubing uses a dual-layer structure: an inner layer of high-quality polyurethane for flexibility and pressure stability, combined with an outer layer made from PVC-based flame retardant material. This design balances mechanical performance with fire safety, rather than sacrificing one for the other.
Compared with standard PU tubing, this structure offers controlled self-extinguishing behavior, reduced molten dripping, and reliable performance in cable trays, drag chains, and control cabinets. For distributors, this makes the product easier to position as a compliant alternative to premium international brands.
No plastic tubing is completely fireproof, including UL94 V-0 materials. The real purpose of flame retardant design is risk control, not absolute prevention. By slowing flame spread and eliminating flaming drips, V-0-rated tubing provides critical time for systems to shut down and for operators to react safely.
Understanding this distinction helps buyers make informed decisions—and helps suppliers communicate value honestly. That is where compliant, well-documented products like FOKCA PU flame retardant tubing play a practical role in modern automation systems.
For more information or to place an order, feel free to contact us.
(FK9026)
 M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
 Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
 Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
 PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
 Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
You May Interest In





Dec 26, 2025 Blog
What Is Vacuum and What Is a Vacuum System


Dec 23, 2025 Blog
How to install compression fitting on copper pipe

Dec 22, 2025 Blog
Can Pneumatic Quick Couplings Be Used for Water














Dec 10, 2025 Blog
How to Choose and Use Rapid Pneumatic Fittings

Dec 08, 2025 Blog
PU Braided Hose for High-Pressure Pneumatic Systems
Dec 05, 2025 Blog
How to Repair a Damaged Hose Using a Hose Mender



Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap