Feb 09, 2026
In pneumatic and fluid transfer systems, selecting the right Nylon Tubing material is critical for achieving long service life and reliable pressure performance. Among the most commonly used materials, PA6 and PA66 are frequently compared due to their similar chemical structures but noticeably different mechanical behaviors. For distributors, equipment engineers, and procurement teams choosing Nylon hose or PA tube solutions, understanding the performance differences helps ensure the tubing matches both pressure and environmental requirements.
Both PA6 and PA66 belong to the polyamide family, widely used in Nylon air hose manufacturing due to their excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance. The key difference lies in molecular arrangement. PA66 has a more tightly packed crystalline structure, resulting in higher rigidity and improved heat resistance, while PA6 offers a more flexible molecular chain, giving it better impact resistance and vibration damping characteristics.
Because of these structural differences, each material is optimized for different operating conditions rather than one universally replacing the other.
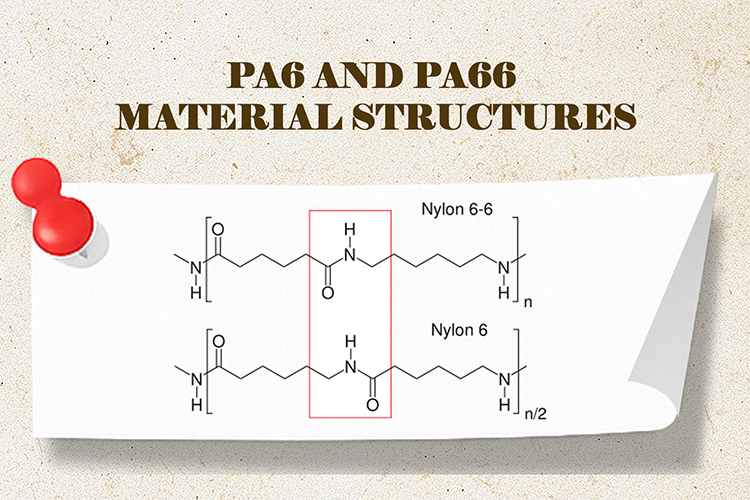
From a mechanical standpoint, PA66 generally provides higher tensile strength and stiffness than PA6. This makes PA66 tubing particularly suitable for applications involving higher pressure, elevated temperatures, or installations where dimensional stability is essential.
In contrast, PA6 offers better impact resistance, making it more suitable for dynamic installations where tubing may be exposed to repeated movement, vibration, or accidental mechanical impact.

Temperature capability is another important factor in Nylon Tubing selection. PA66 maintains structural stability at higher temperatures, which helps prevent deformation in hot industrial environments such as engine compartments or heated processing equipment. It also demonstrates superior creep resistance, meaning it better resists long-term deformation under continuous pressure.
However, when applications involve intermittent shock loads or fluctuating mechanical stress, PA6 tubing often performs more reliably due to its higher toughness and damping characteristics.
The following simplified comparison illustrates the practical engineering differences between the two materials:
| Property | PA6 | PA66 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | Good | Higher |
| Rigidity | Moderate | Higher |
| Impact resistance | Higher | Moderate |
| Heat resistance | Good | Better |
| Creep resistance | Good | Higher |
| Vibration damping | Better | Moderate |
| Wear resistance | Good | Better |
This comparison shows that PA66 excels in strength, stiffness, heat resistance, and wear performance, while PA6 performs better in impact strength and mechanical damping.
When selecting Nylon hose materials, engineers typically match the material to the operating environment:
◆Use PA66 tubing in high-pressure pneumatic lines, elevated temperature zones, or static installations requiring high dimensional stability
◆Use PA6 tubing in moving machinery, robotic equipment, or installations where vibration and repeated bending occur
◆Consider flexibility, temperature range, and installation movement together rather than evaluating strength alone
Manufacturers offering both PA6 and PA66 Nylon Tubing product ranges allow equipment designers and distributors to select the most suitable material without changing tubing dimensions or connector systems.
Although PA66 is generally stronger than PA6, the optimal choice depends on operating conditions. Strength advantages of PA66 come at the cost of slightly lower impact resistance and damping performance, which means PA6 remains highly valuable in dynamic pneumatic systems.
For procurement and engineering teams comparing PA tube specifications, reviewing mechanical strength, temperature exposure, and installation movement together ensures the selected tubing delivers both performance reliability and cost efficiency across the system lifecycle.
(FK9026)
 M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
 Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
 Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
 PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
 Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
You May Interest In



Feb 06, 2026 Blog
How to Judge the Quality of Polyurethane Tubing






Jan 06, 2026 Blog
How to Measure NPT Threads Accurately on a Fitting






Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap