Dec 31, 2025
In industrial fluid systems, connection methods are rarely a minor detail. Whether the application involves pneumatic automation, water distribution, or light hydraulic circuits, the choice between compression fittings and welding can influence installation efficiency, maintenance cost, system safety, and long-term reliability. For distributors, engineers, procurement managers, and factory owners, understanding how these two approaches differ is essential before making a purchasing or design decision.
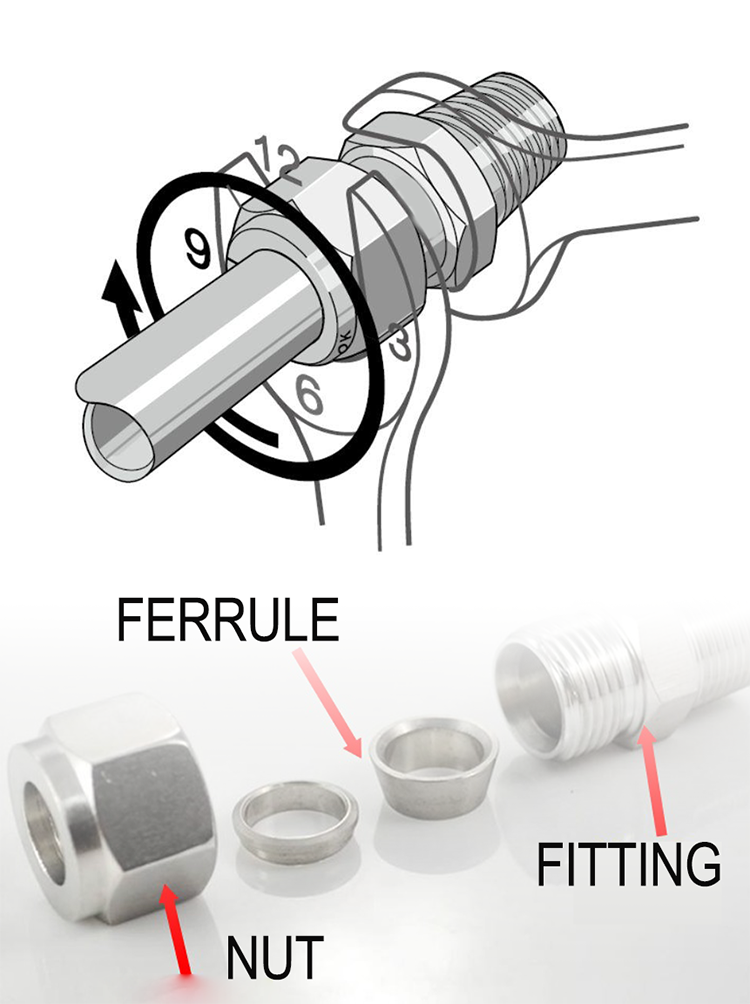
Compression fittings rely on mechanical sealing rather than heat or fusion. When the nut is tightened, the ferrule compresses onto the tube’s outer surface, creating a tight seal that prevents leakage. This structure explains why compression fittings are widely used in industrial automation, compressed air lines, and plumbing systems where flexibility and serviceability matter.
From an engineering perspective, compression fittings offer predictable performance when installed correctly. They do not alter the tubing material through heat, which helps preserve mechanical properties. This makes them suitable for mixed-material systems, including metal tubing, plastic compression fittings, and polyethylene compression fittings used in water or chemical transfer lines.
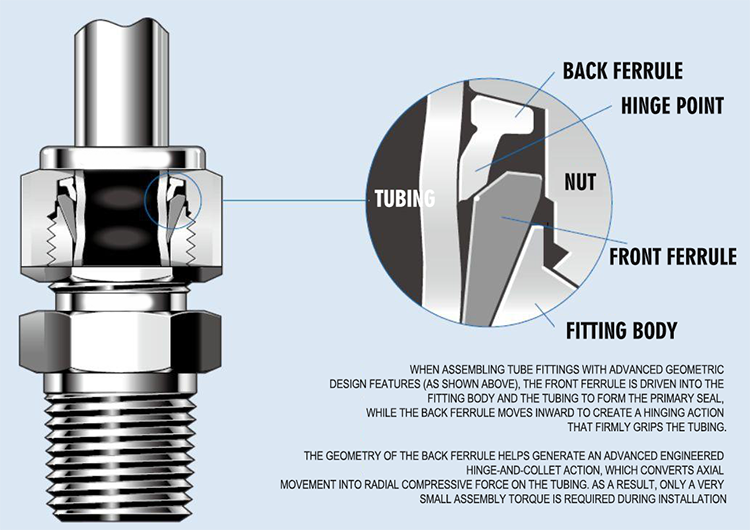
Not all compression fittings are the same, and choosing the wrong type can lead to premature failure or unnecessary cost. Standard designs are commonly used in pneumatic systems, while reinforced structures are selected for higher mechanical stress.
Type B compression fittings, for example, use enhanced ferrule geometry to improve holding strength and vibration resistance. These are often specified in industrial machinery where cyclic motion or frequent pressure changes are present. In plumbing systems, plumbing compression fittings PVC designs are popular because they allow fast installation without solvent welding, especially in confined spaces.
For water distribution, a compression fitting for water line applications is often preferred because it allows disassembly during maintenance. Polyethylene compression fittings are also widely used in outdoor or corrosion-sensitive environments due to their chemical stability and resistance to scaling.
Welding creates a permanent joint by fusing metal components together at high temperature. Once completed, the connection becomes part of the pipe itself, offering excellent resistance to pressure, vibration, and extreme temperatures. For this reason, welding is often chosen for high-pressure hydraulic pipelines, high-temperature processes, or fixed installations that are unlikely to be modified.
However, permanence is both a strength and a limitation. Welding requires skilled labor, strict safety procedures, and inspection. Any design change or repair typically means cutting the pipe and re-welding, which increases downtime and cost. From a procurement standpoint, the initial joint may appear robust, but lifecycle cost can rise quickly if system flexibility is required.

When comparing compression fittings plumbing solutions with welding, the differences become clearer in daily operation rather than on paper specifications.
| Comparison Factor | Compression Fittings | Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Installation time | Very fast | Slow |
| Skill requirement | Low | High |
| System flexibility | High | Very low |
| Maintenance | Easy disassembly | Difficult |
| Modification cost | Low | High |
| Long-term strength | High (proper installation) | Very high |
Compression fittings are particularly valuable in systems where maintenance, upgrades, or layout changes are expected. Pneumatic automation lines, OEM machinery, and laboratory equipment often benefit from compression fitting diagram–based layouts that allow quick troubleshooting and component replacement.
Plastic compression fittings and polyethylene compression fittings are frequently used in water treatment, food equipment, and light chemical systems where corrosion resistance and cleanliness are priorities. For distributors and procurement managers, these products also simplify inventory management because one fitting design can serve multiple tubing materials.
In many cases, the ability to disassemble and reuse fittings reduces long-term operating costs, even if the initial unit price appears higher than welded joints.
FOKCA Automation provides a comprehensive range of tubing and fitting solutions designed to support both performance and efficiency in industrial systems. For customers using compression fittings, FOKCA supplies compatible pneumatic tubing and connection components that ensure consistent sealing and long service life.
With OEM and ODM capabilities, FOKCA supports customized dimensions, materials, and packaging for distributors and equipment manufacturers. This flexibility helps customers align compression fittings plumbing solutions with their specific system requirements, reducing assembly time and minimizing field failures.
For more information or to place an order, feel free to contact us.
(FK9026)
 M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
 Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
 Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
 PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
 Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
You May Interest In





Dec 26, 2025 Blog
What Is Vacuum and What Is a Vacuum System



Dec 23, 2025 Blog
How to install compression fitting on copper pipe

Dec 22, 2025 Blog
Can Pneumatic Quick Couplings Be Used for Water










Dec 10, 2025 Blog
How to Choose and Use Rapid Pneumatic Fittings

Dec 08, 2025 Blog
PU Braided Hose for High-Pressure Pneumatic Systems
Dec 05, 2025 Blog
How to Repair a Damaged Hose Using a Hose Mender




Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap