Dec 19, 2025
In pneumatic systems, a project can be delayed by something as small as a thread mismatch. An engineer may have selected the right cylinder, valve, and tubing, only to find that the ports cannot be connected because the thread type or size does not match. This situation is common in global equipment manufacturing, where machines integrate components from different standards. The most practical solution is the use of a thread adapter, a functional category of pipe fittings designed specifically for thread conversion and compatibility.
For distributors, equipment engineers, procurement teams, and end users, understanding how thread adapters and pneumatic push in fittings work is essential to keeping installations reliable, leak-free, and cost-efficient.
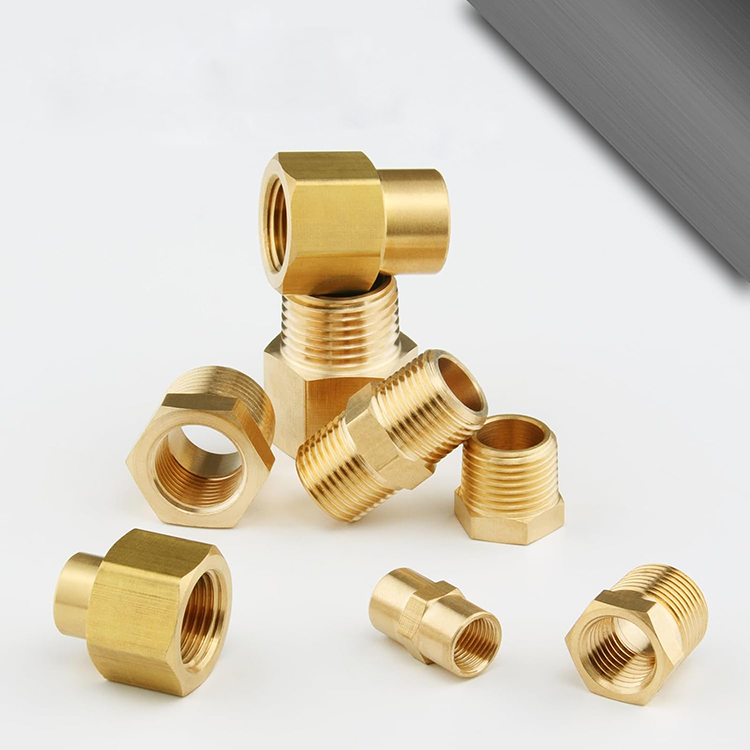

Thread mismatch is not a quality issue—it is a standards issue. Pneumatic components are produced under different regional thread systems, and mixing them in one machine is almost unavoidable. A valve imported from Europe may use BSPP threads, while a locally sourced manifold might be tapped for NPT. Even within the same thread family, port sizes often differ.
In real installations, mismatch usually shows up in three ways:
1.male threads that should be female
2.ports that are physically too large or too small
3.threads that look similar but seal differently.
Without a proper pipe fitting solution, installers may attempt force-fitting, which almost always leads to leaks or cracked ports.
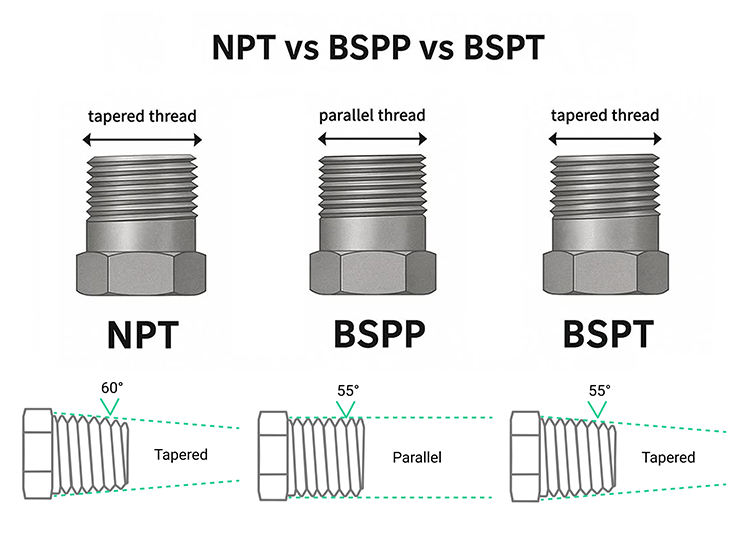
A thread adapter, is a specialized type of pipe fitting used to connect two components with incompatible threads. Unlike standard straight fittings, its core purpose is conversion rather than simple connection. In pneumatic systems, these adapters must handle not only mechanical fit but also air pressure, sealing performance, and vibration.
From a functional perspective, thread adapters fall under the broader category of pipe fittings, but they are often overlooked during system design. In practice, they serve as problem-solvers on the shop floor, enabling fast installation without re-machining ports or replacing expensive components.

One of the most common needs is gender conversion. For example, when both the valve and the cylinder have female ports, installation becomes impossible without an intermediary. A male-to-male or female-to-male thread adapter solves this instantly.
This type of pipe fitting is widely used in retrofits and maintenance work, especially when replacing legacy components. For distributors and maintenance teams, keeping common gender-conversion adapters in stock can significantly reduce downtime.
Another frequent issue is thread size mismatch. Larger ports are often used on air preparation units, while smaller ports are common on cylinders and sensors. A typical example is converting G1/2 to G1/4, allowing a large air source to connect cleanly to compact downstream components.
From a system design perspective, size conversion adapters help maintain airflow while adapting to space constraints. When properly selected, they avoid unnecessary pressure drop and ensure stable air delivery. High-quality pipe fittings are machined with accurate internal bores to balance compact size with flow efficiency.
Thread type conversion is the most critical—and the most misunderstood—application. BSPP, BSPT, NPT, and Metric threads may appear similar, but they differ in thread angle, pitch, and sealing method. Direct connection often leads to micro-leaks that worsen over time.
A dedicated thread adapter allows safe conversion between standards without damaging ports. In international projects, this is especially important for OEMs and agents who integrate components from multiple suppliers. According to industry standard guidelines from ISO thread specifications, proper conversion fittings are essential for long-term sealing reliability.
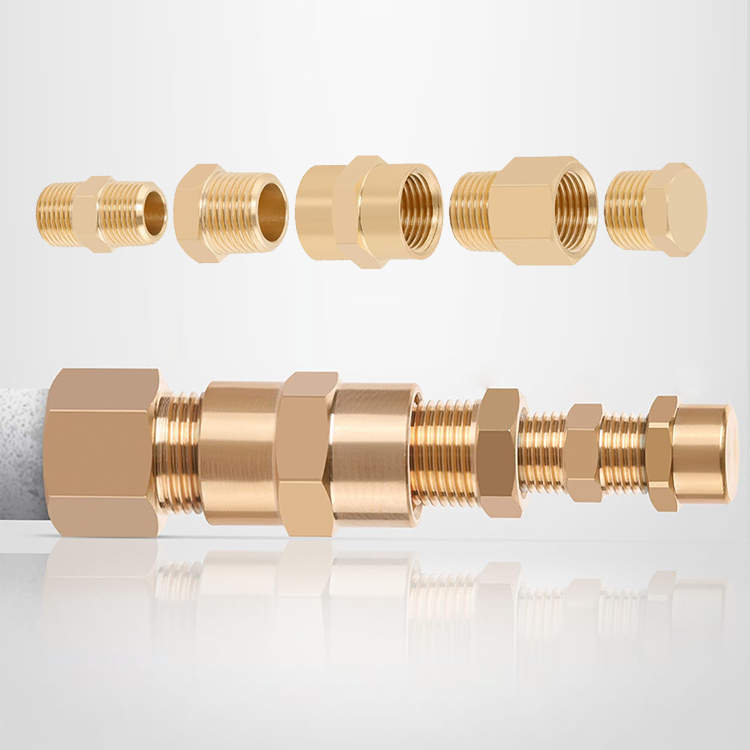

In modern pneumatic systems, pneumatic push in fittings are widely used for their speed and ease of installation. However, these fittings still rely on threaded ports to connect to valves, cylinders, and manifolds. When a push in fitting does not match the port thread, a thread adapter becomes the bridge.
A typical setup may include:
◆A thread adapter to convert the port thread
◆A push in fitting to connect the air tube
This combination allows engineers to standardize tubing while remaining flexible on port standards. For equipment builders, this approach reduces inventory complexity and simplifies future maintenance.

Not all thread adapters are equal. Material selection directly affects durability and application suitability. Common options include nickel-plated brass, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy. Each has its role depending on pressure, environment, and media.
Sealing method is equally important. Some pipe fittings rely on thread taper for sealing, while others require O-rings or sealing washers. In pneumatic applications, improper sealing choice is one of the leading causes of air leakage. Experienced engineers often select adapters with integrated sealing to reduce installation variability.
When choosing a thread adapter, the first step is to clearly identify both sides of the connection: thread type, size, and gender. Guessing based on appearance is risky, especially between BSPT and NPT. Using thread gauges or supplier documentation saves time and prevents rework.
For procurement teams and distributors, it is wise to focus on high-rotation conversion types, such as BSP to NPT and common size reducers. Stocking standardized, high-quality pipe fittings improves customer satisfaction and reduces returns caused by improper fit.
As a global pneumatic component supplier, FOKCA Automation designs thread adapters and pipe fittings with OEM and distributor needs in mind. Our products are manufactured with precise threading tolerances, stable materials, and compatibility with common pneumatic push in fittings.
Beyond standard adapters, FOKCA supports OEM/ODM customization, including special thread combinations, non-standard lengths, and application-specific sealing solutions. This flexibility is especially valuable for agents and equipment manufacturers working across multiple markets with different standards.
Solving Thread Mismatch Is About System Reliability.Thread mismatch is not just an installation inconvenience—it directly impacts system reliability, air efficiency, and maintenance cost. A properly selected thread adapter allows components to work together as a complete pneumatic system, regardless of their origin.
For more detail you can contact us.
(FK9026)
 PUAS Polyurethane Tubing: Flexible, Durable, and Anti-Static Solution for Industrial Applications
PUAS Polyurethane Tubing: Flexible, Durable, and Anti-Static Solution for Industrial Applications
 Which Pneumatic Fittings Perform Best in High-Vibration Applications
Which Pneumatic Fittings Perform Best in High-Vibration Applications
 Why Pneumatic Tubing Should Not Be Bent Immediately After an SMC One Touch Fitting
Why Pneumatic Tubing Should Not Be Bent Immediately After an SMC One Touch Fitting
 Why Aluminum Foil Is Added to PUFR Flame-Resistant Hose and How It Improves Fire Performance
Why Aluminum Foil Is Added to PUFR Flame-Resistant Hose and How It Improves Fire Performance
 Why Nylon Hose Leaks: The Real Causes Behind Air Loss at Fittings
Why Nylon Hose Leaks: The Real Causes Behind Air Loss at Fittings
You May Interest In







Dec 10, 2025 Blog
How to Choose and Use Rapid Pneumatic FittingsLinks: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap