Dec 23, 2025
In water supply systems, copper remains one of the most trusted pipe materials thanks to its hygiene, durability, and thermal stability. However, the reliability of the system depends just as much on how those copper pipes are connected. For many distributors, engineers, and procurement managers, compression fittings have become a preferred solution—provided the right materials and installation practices are used.
Copper compression fittings create a mechanical seal by compressing a ferrule (olive) between the fitting body and the copper tubing. This simple principle offers several practical advantages over welded or soldered joints.
For installers and equipment engineers, copper pipe compression fittings eliminate the need for open flames, flux, or filler metals. This makes them especially suitable for confined spaces, retrofits, or environments where hot work permits are restricted. From a maintenance perspective, compression joints can be disassembled and reinstalled, which is impossible with soldered connections.
In modern plumbing and equipment systems, copper plumbing compression fittings are commonly used in water distribution, filtration units, beverage equipment, and OEM assemblies where speed and consistency matter.
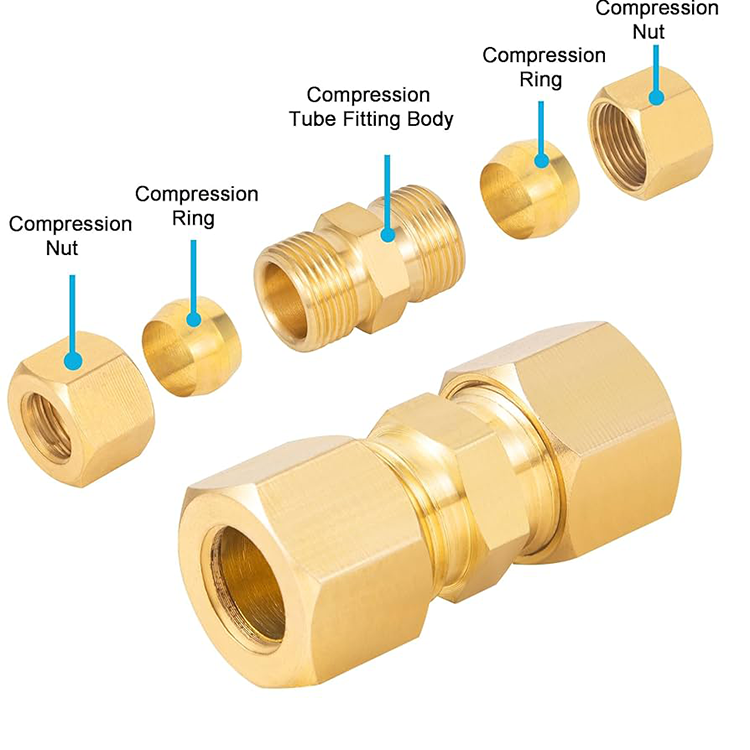
One of the most critical—but often overlooked—factors in compression fitting selection is material compatibility. While compression fittings may look similar externally, their metallurgy directly affects system lifespan.
Carbon steel compression fittings should not be used on copper pipes. When carbon steel comes into contact with copper in the presence of water, a galvanic couple is formed. Copper is more noble than carbon steel, causing the steel component to corrode preferentially. Over time, this electrochemical reaction accelerates corrosion at the joint, often damaging the copper pipe itself near the connection point.
This type of failure is particularly common in water systems with minerals or fluctuating temperatures, and it is difficult to detect until leakage occurs.
To avoid galvanic corrosion and ensure long-term reliability, the industry standard is to use materials that are electrochemically compatible with copper.
Brass compression couplings are the most widely used option. Brass has excellent corrosion resistance in potable water systems and a galvanic potential close to copper, minimizing electrochemical reactions. This is why brass compression coupling solutions dominate residential and industrial plumbing markets.
For applications requiring enhanced corrosion resistance or cleaner surfaces, nickel-plated copper fittings are another reliable choice. The nickel layer improves surface hardness and appearance while maintaining compatibility with copper tubing.
In more demanding environments—such as food processing equipment or corrosive water conditions—stainless steel compressionfittings can also be used with copper pipes, provided the grade is suitable and properly specified.
Correct installation is essential for achieving a leak-free seal. Even the best copper tubing compression fittings can fail if improperly installed.
The copper pipe must be cut squarely, with burrs fully removed from both inner and outer edges. Any deformation prevents the ferrule from seating evenly. After sliding the nut and ferrule onto the pipe, the fitting body is inserted until it bottoms out.
Tightening torque is critical. Over-tightening can deform the ferrule excessively, damaging the copper tube, while under-tightening results in leakage. Many manufacturers recommend tightening by hand first, then applying a controlled additional rotation using a wrench. Consistency matters more than brute force.
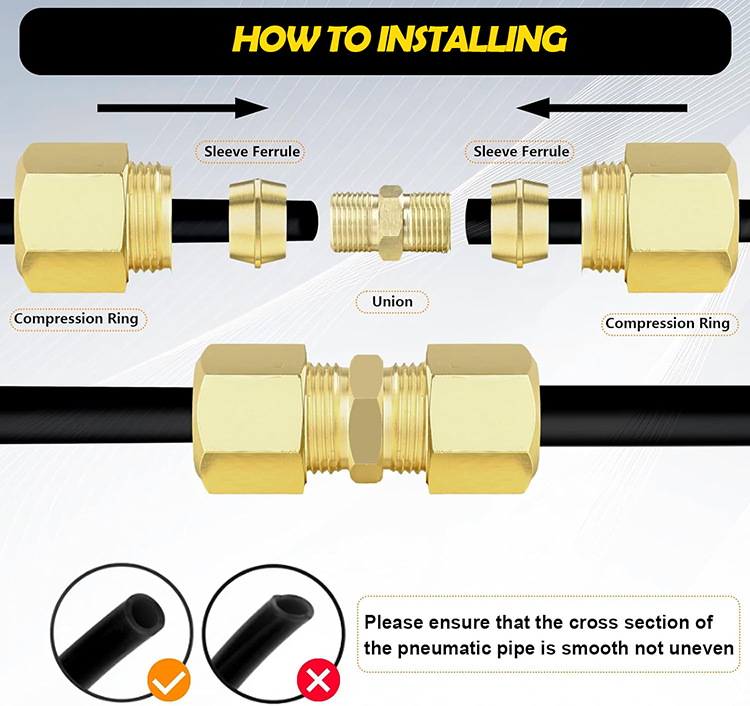
Traditional soldering has long been associated with copper piping, but its limitations are increasingly apparent in modern systems.
Soldered joints require heat, skilled labor, and strict cleanliness. In water systems, residual flux can contribute to internal corrosion if not fully flushed. Rework is time-consuming, often requiring pipe replacement.
By contrast, compression couplings allow fast installation with minimal tools and no heat. For OEM equipment, this reduces assembly time and improves repeatability. For distributors and end users, it means fewer installation errors and easier field servicing.
While soldered joints may offer slightly lower material cost, compression fittings often provide lower total installed cost when labor, downtime, and maintenance are considered.
Copper compression fittings are especially well suited for low- to medium-pressure water systems, potable water lines, filtration systems, and equipment connections where future disassembly may be required.
They are widely used in vending machines, beverage dispensers, laboratory equipment, and compact water modules. In these applications, the combination of copper tubing and compatible compression fittings delivers both hygiene and serviceability.
For distributors, offering multiple material options—brass, nickel-plated copper, and stainless steel—allows better alignment with customer requirements and regulatory standards.
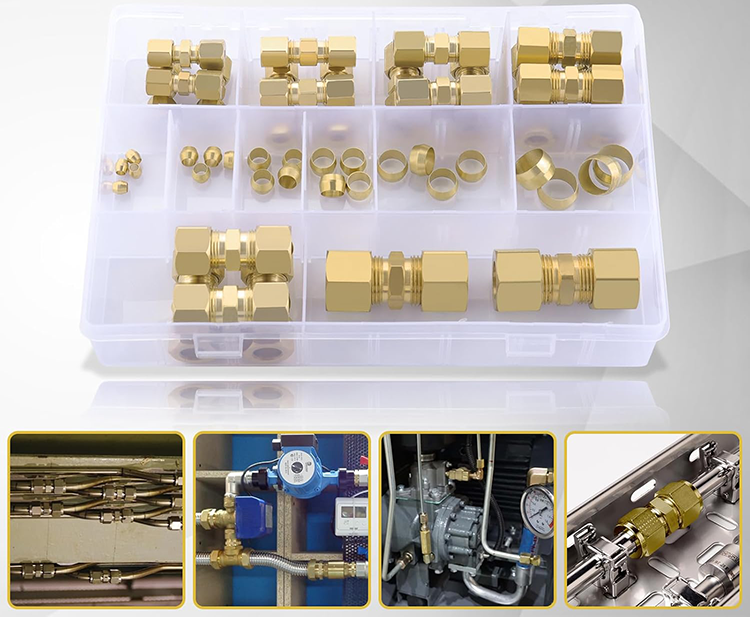

As a global supplier of fluid and pneumatic connection components, FOKCA Automation provides a complete range of compression fittings, couplings, and compatible tubing materials. Our product portfolio includes brass compression couplings, stainless steel fittings, and precision-machined connectors designed for copper pipe applications.
Beyond standard products, FOKCA supports OEM/ODM customization, helping equipment manufacturers and system integrators specify thread types, dimensions, and materials that match real operating conditions. This system-level approach reduces mismatch risks and improves long-term performance.
Combined with our pneumatic hoses, quick couplings, valves, and actuators, FOKCA enables customers to source reliable connection solutions from a single, technically aligned supplier.
Installing compression fittings on copper water pipes is not just about convenience—it is about material compatibility, corrosion control, and lifecycle cost. Selecting brass, nickel-plated copper, or stainless steel fittings avoids galvanic corrosion risks that carbon steel introduces.
When installed correctly, copper pipe compression fittings offer a clean, serviceable, and durable alternative to soldering, especially in modern equipment and modular water systems. For engineers, buyers, and distributors alike, understanding these details helps ensure that a simple connection does not become a future failure point.
In water systems, reliability often comes down to the smallest components—and compression fittings are no exception.
For more information or to place an order, feel free to contact us.
(FK9026)
 PUAS Polyurethane Tubing: Flexible, Durable, and Anti-Static Solution for Industrial Applications
PUAS Polyurethane Tubing: Flexible, Durable, and Anti-Static Solution for Industrial Applications
 Which Pneumatic Fittings Perform Best in High-Vibration Applications
Which Pneumatic Fittings Perform Best in High-Vibration Applications
 Why Pneumatic Tubing Should Not Be Bent Immediately After an SMC One Touch Fitting
Why Pneumatic Tubing Should Not Be Bent Immediately After an SMC One Touch Fitting
 Why Aluminum Foil Is Added to PUFR Flame-Resistant Hose and How It Improves Fire Performance
Why Aluminum Foil Is Added to PUFR Flame-Resistant Hose and How It Improves Fire Performance
 Why Nylon Hose Leaks: The Real Causes Behind Air Loss at Fittings
Why Nylon Hose Leaks: The Real Causes Behind Air Loss at Fittings
You May Interest In


Dec 22, 2025 Blog
Can Pneumatic Quick Couplings Be Used for Water











Dec 05, 2025 Blog
How to Repair a Damaged Hose Using a Hose Mender
Dec 08, 2025 Blog
PU Braided Hose for High-Pressure Pneumatic Systems







Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap