Feb 11, 2026
In modern automation lines, tubing installed inside moving cable carriers must withstand continuous bending, pulling, and vibration. Standard soft tubing often fails early due to fatigue cracking or excessive elongation. For this reason, many engineers specify Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube made from 95A or 98A PU materials, which provide improved structural stability and longer service life in dynamic installations.
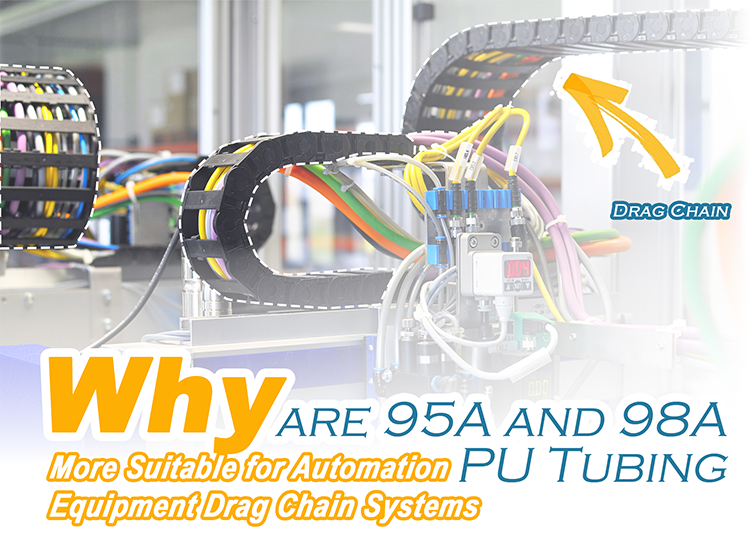
Drag chains create repeated cyclic motion where pneumatic tubing experiences bending thousands of times per day. Under these conditions, tubing with insufficient hardness tends to stretch or flatten, causing airflow instability and premature wear. A properly selected PU Pneumatic Hose must maintain dimensional stability while remaining flexible enough to handle continuous motion.
In high-speed automation equipment such as pick-and-place robots or CNC tool changers, tubing fatigue resistance directly affects system uptime. Higher-hardness polyurethane tubing significantly reduces deformation under repeated stress, which improves long-term reliability.
Compared with softer grades such as 80A or 85A, 95A PU Tubing and 98A PU Tubing offer stronger molecular bonding and higher tensile strength. These material characteristics provide better resistance to mechanical fatigue and external pulling forces common in cable carrier installations.
◆Higher tensile strength for resisting drag-chain pulling forces
◆Improved abrasion resistance against carrier track friction
◆ower elongation under load, maintaining stable airflow performance
◆Longer service intervals, reducing maintenance costs
These properties make high-hardness tubing the preferred option in most dynamic pneumatic routing systems.
The following table shows the typical performance differences observed in industrial applications (data ranges based on industry material reports):
| Hardness (Shore A) | Flexibility | Tensile Strength | Drag Chain Durability | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80A | Very high | Medium | Moderate | Tight routing areas |
| 85A | High | Medium-high | Good | General automation |
| 95A | Balanced | High | Very high | Standard drag chains |
| 98A | Moderate | Very high | Maximum durability | High-load motion systems |
Fatigue cracking is one of the most common causes of pneumatic tubing failure inside cable carriers. When softer tubing repeatedly stretches beyond its elastic recovery limit, micro-cracks gradually develop and eventually lead to leakage. Using 98A PU Tubing minimizes elongation during each motion cycle, significantly extending operating life in robotic and automated production equipment.
For installations involving high travel speed or long stroke lengths, engineers often combine Industrial PU Hose with abrasion-resistant carrier guides to maximize lifetime performance.

Higher-hardness tubing also improves routing stability inside drag chains. Softer tubing tends to twist or overlap during operation, increasing friction and wear. 95A or 98A Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube maintains a more stable routing path, reducing internal cable-carrier interference and improving airflow consistency.
When selecting tubing for new automation equipment, engineers typically match tubing hardness with carrier motion intensity. Medium-speed systems often perform well with 95A tubing, while heavy-duty robotics or long-travel gantry systems benefit from 98A grades.
Selecting the correct tubing hardness is not only a material decision but also a lifecycle cost consideration. While softer tubing may appear easier to install initially, frequent replacement and downtime can quickly increase operating costs. High-hardness polyurethane tubing delivers better long-term performance in dynamic motion environments, especially where continuous operation is critical.
For automation equipment operating under continuous motion, 95A and 98A polyurethane tubing remains the most reliable choice for drag chain pneumatic routing, balancing durability, airflow stability, and service life.
(FK9026)
 M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
 Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
 Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
 PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
 Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
You May Interest In

May 07, 2025 Blog
Comprehensive Analysis of Pneumatic Push in Fittings
Apr 22, 2025 Blog
Solution for Nylon Tube
Apr 16, 2025 Blog
PVC Tubing vs. Polyurethane Tubing
Apr 10, 2025 Blog
What is the difference between pu and pvc
Feb 24, 2025 Blog
How to Identify Hydraulic Quick Couplers?
Jan 21, 2025 Blog
How to Measure Pipe Thread?
Jan 16, 2025 Blog
What Is Pipe thread?
Dec 04, 2024 Blog
Application Of Tube Fitting

Jun 26, 2023 Blog
What Is The Difference Between LLDPE And LDPE?
Jan 17, 2023 Blog
What Are The Classification Of Plastics?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap