Dec 22, 2025
In modern pneumatic systems, plastic pneumatic quick coupling products are often taken for granted. They look simple, cost-effective, and easy to install, yet behind that simplicity is a carefully engineered structure designed to balance air tightness, durability, repeatable assembly, and production efficiency. For distributors, engineers, and procurement managers alike, understanding the internal components of push-to-connect fittings is not just technical curiosity—it directly affects product selection, system reliability, and long-term cost control.
This article breaks down the core components of pneumatic quick couplings, explaining how each part works, what materials are commonly used, and why design details matter in real industrial applications. Along the way, we connect structure to performance, and performance to sourcing decisions—especially in OEM and distribution scenarios.
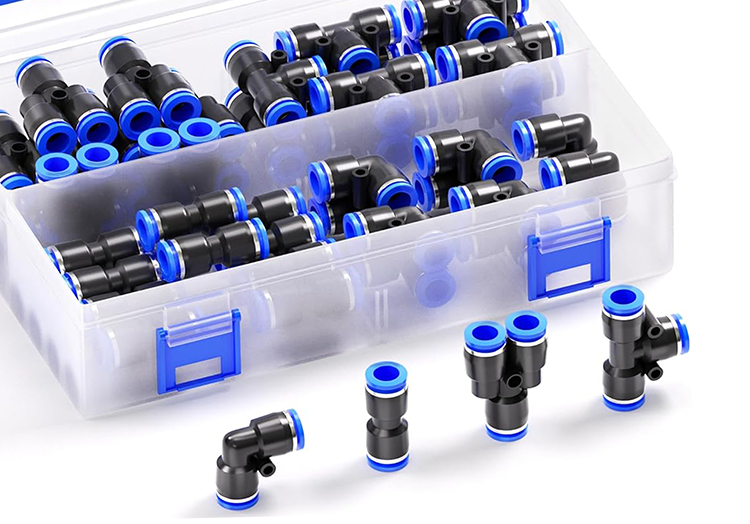

A pneumatic system is only as reliable as its smallest connection point. In automated assembly lines, packaging machines, or food-processing equipment, a single poorly designed pneumatic quick coupling can become the source of air leakage, unplanned downtime, or repeated maintenance. Engineers often focus on cylinder size or valve flow rate, but the internal structure of push-to-connect fittings determines whether those components perform as intended.
From a commercial perspective, distributors and purchasing managers face another layer of complexity. Externally similar fittings may vary significantly in internal design, material selection, and tolerance control. These hidden differences explain why some fittings last years under vibration, while others fail prematurely in the same application.

At the core of every plastic pneumatic quick coupling is the main body. This component defines the fitting’s geometry, pressure rating, and compatibility with tubing and ports. Typically molded from engineering plastics such as PBT, PA66, or reinforced nylon, the body must provide both mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
In high-quality push-to-connect fittings, the body is designed with precision-molded internal chambers that guide airflow smoothly while securely housing sealing and gripping elements. Poorly designed bodies often show uneven wall thickness or rough internal surfaces, increasing turbulence and stress concentration. Over time, these flaws can lead to micro-cracks or deformation, especially in systems operating near pressure limits.
For OEM customers, body design also affects customization. FOKCA’s OEM/ODM production capabilities allow custom port shapes, special thread standards, and compact geometries, helping equipment manufacturers optimize layout without sacrificing reliability.
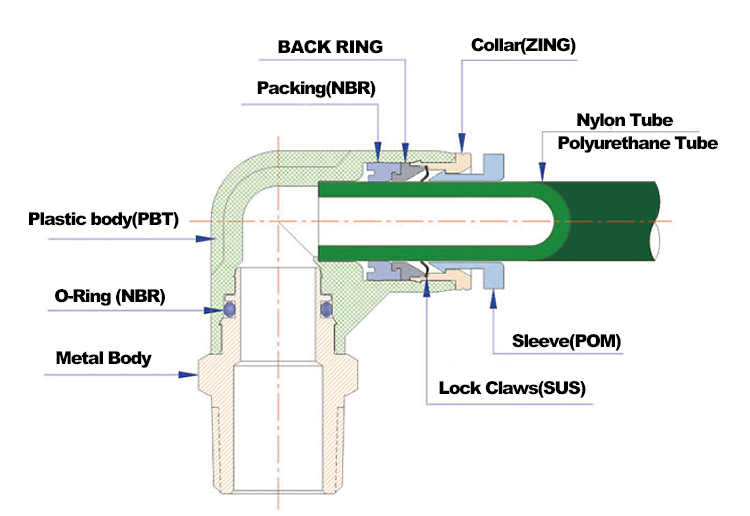
The collet, sometimes called the release ring, is the most visible moving part of a push-to-connect fitting. Its role appears simple—press to release the tube—but its internal interaction with other components is critical. The collet transmits axial force to disengage the gripping mechanism while maintaining alignment.
High-performance pneumatic quick coupling designs use wear-resistant plastic or plastic-metal hybrid collets. The surface finish and elasticity of this part influence both user experience and service life. A collet that deforms too easily may release unintentionally under vibration; one that is too rigid can make tube removal difficult, increasing maintenance time.
From a distributor’s standpoint, collet quality often correlates with customer satisfaction. End users quickly notice whether fittings feel “loose” or “solid” during installation, even if they cannot identify the internal reason.
Hidden beneath the collet lies one of the most critical elements: the gripping teeth. These stainless steel claws bite into the outer surface of the tube, preventing pull-out under pressure. In a well-designed pneumatic quick coupling, the teeth are angled to allow easy insertion but resist axial force in the opposite direction.
Material choice here is non-negotiable. Stainless steel provides corrosion resistance and elastic recovery, allowing the teeth to maintain grip over thousands of insertion cycles. Lower-grade alternatives may flatten or corrode, especially in humid or chemically aggressive environments.
In industrial practice, tube pull-out failures are often misattributed to incorrect tubing size, when the real issue lies in poor tooth geometry or inconsistent heat treatment. This is one area where reputable manufacturers distinguish themselves through process control rather than appearance.

The sealing function of push-to-connect fittings depends almost entirely on the O-ring. Positioned just inside the gripping mechanism, the O-ring forms a radial seal around the tube, preventing air leakage even under fluctuating pressure.
Common materials include NBR for general industrial use, EPDM for water or mild chemicals, and FKM for high-temperature or aggressive media. The choice of O-ring material directly impacts service life and application compatibility. An otherwise well-built pneumatic quick coupling can fail prematurely if the seal material is poorly matched to the working environment.
Equally important is groove design. Precision-machined or molded grooves ensure the O-ring is neither over-compressed nor under-loaded. This detail often separates fittings suitable for long-term OEM installations from those intended only for light-duty use.
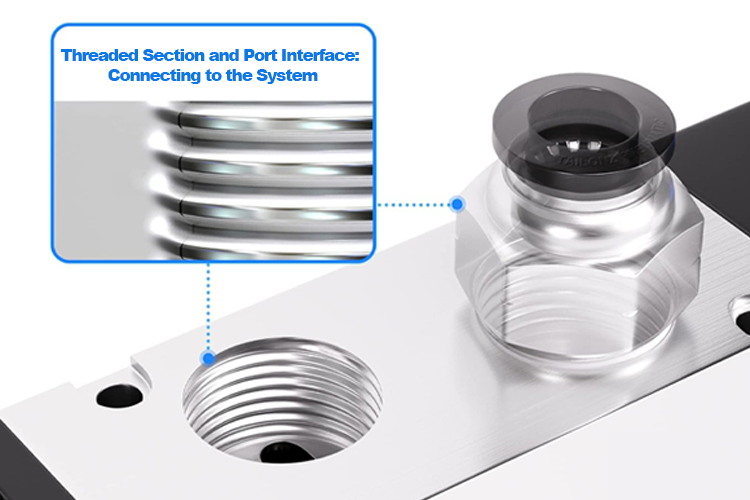
The threaded end of a push-to-connect fitting connects it to valves, cylinders, or manifolds. While seemingly straightforward, this section must balance sealing, mechanical strength, and compatibility with global standards such as BSPP, BSPT, NPT, or metric threads.
Quality manufacturers control thread tolerances tightly and often integrate pre-applied thread sealant or precision sealing faces. This reduces installation variability and minimizes the risk of overtightening, a common cause of cracked plastic bodies.
For distributors serving international markets, offering fittings with multiple thread standards—without compromising internal structure—is a key competitive advantage.

When these components work in harmony, the result is a pneumatic quick coupling that installs quickly, seals reliably, and withstands years of operation. When one element is compromised, failures cascade. A slightly undersized O-ring increases leakage, which leads to compressor overuse. A weak gripping tooth causes tube movement, accelerating seal wear.
In one packaging equipment project, an OEM replaced generic fittings with higher-grade push-to-connect fittings featuring reinforced bodies and upgraded seals. According to internal maintenance data (equipment lifecycle analysis), air consumption dropped by 8–12%, and unplanned downtime related to pneumatic connections was nearly eliminated within the first year.

Plastic pneumatic quick coupling fittings may be small, but their internal structure reflects decades of pneumatic engineering evolution. By understanding the role of each component—from body and collet to seals and gripping teeth—buyers and engineers can make decisions based on performance rather than appearance.
In an industry where reliability and efficiency define competitiveness, component-level insight turns a simple fitting into a strategic choice. And for those building long-term supply relationships, that insight is often what separates a supplier from a partner.
As a global supplier of pneumatic components, FOKCA integrates material selection, mold design, and assembly control into a unified manufacturing process. Our plastic pneumatic quick coupling products are designed for compatibility with standard tubing systems, while offering OEM/ODM flexibility in structure, material, and branding.
For partners seeking differentiation, FOKCA supports customized push-to-connect fittings, including special sealing materials, compact designs, and application-specific modifications. This approach allows distributors and OEMs to offer solutions tailored to real operating conditions, not just catalog specifications.
For more detail you can contact us.
(FK9026)
 PUAS Polyurethane Tubing: Flexible, Durable, and Anti-Static Solution for Industrial Applications
PUAS Polyurethane Tubing: Flexible, Durable, and Anti-Static Solution for Industrial Applications
 Which Pneumatic Fittings Perform Best in High-Vibration Applications
Which Pneumatic Fittings Perform Best in High-Vibration Applications
 Why Pneumatic Tubing Should Not Be Bent Immediately After an SMC One Touch Fitting
Why Pneumatic Tubing Should Not Be Bent Immediately After an SMC One Touch Fitting
 Why Aluminum Foil Is Added to PUFR Flame-Resistant Hose and How It Improves Fire Performance
Why Aluminum Foil Is Added to PUFR Flame-Resistant Hose and How It Improves Fire Performance
 Why Nylon Hose Leaks: The Real Causes Behind Air Loss at Fittings
Why Nylon Hose Leaks: The Real Causes Behind Air Loss at Fittings
You May Interest In








Dec 05, 2025 Blog
How to Repair a Damaged Hose Using a Hose Mender
Dec 08, 2025 Blog
PU Braided Hose for High-Pressure Pneumatic Systems
Dec 10, 2025 Blog
How to Choose and Use Rapid Pneumatic Fittings

Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap