Dec 05, 2025
Soft hoses fail more often than most people expect. A small crack caused by abrasion, bending fatigue, or chemical exposure can stop a machine, interrupt air or water supply, and increase downtime costs.
For equipment engineers, distributors, and plant maintenance teams, a hose mender—also known as two-barb connector, double-barb fitting, mender hose, hose mend—is one of the quickest ways to restore normal flow.
When paired with hose clamps, it reconnects two cut hose ends and provides a reliable seal for both air and liquid systems.
The following sections explain how to choose the right material, when to use push-in fittings instead of a barb-type mender, and how to install a union fitting properly.
These details help buyers evaluate quality and help engineers perform fast and safe hose repair on-site.
Hoses fail for several predictable reasons:
• Constant bending that weakens the wall structure
• Long-term friction against metal surfaces
• Chemical corrosion from oil, water additives, or cleaning agents
• Accidental cuts during maintenance
When a full hose replacement is inconvenient—such as when a 20-meter hose is embedded inside a machine—using a hose repair connector is often the fastest, most cost-effective solution.
A mender hose restores flow in minutes, allowing the production line to resume without waiting for new parts or conducting major disassembly.
A packaging factory in Southeast Asia recorded an average restart time of under five minutes using brass hose menders to fix cooling-water hoses.
This simple tool allowed maintenance staff to avoid extended shutdowns and prevented considerable production loss.
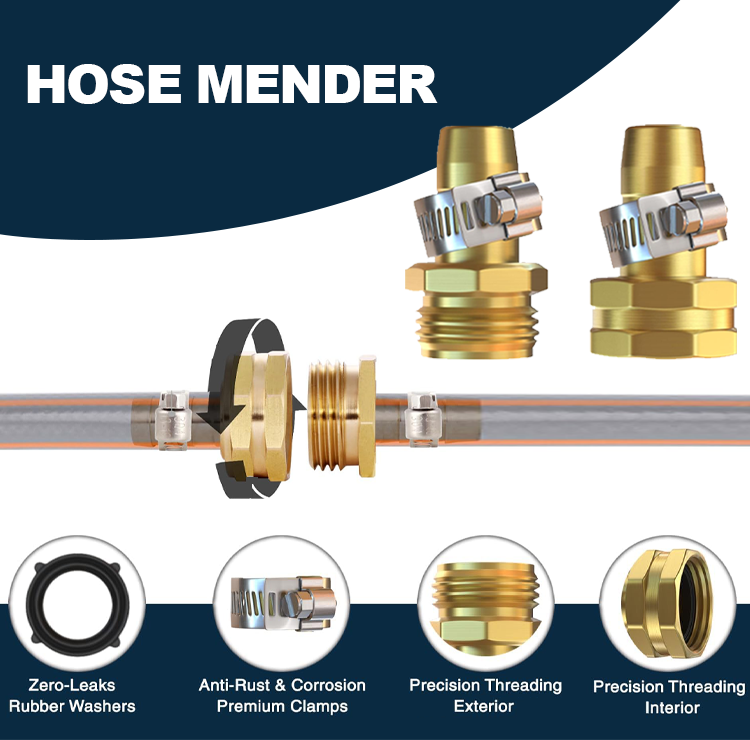
A typical hose mender features two identical barbed ends—commonly referred to as two-barb / two-tail / two-mouse-tail fittings. Each side is inserted into the hose, and hose clamps secure the joint.
The barb profile increases friction, preventing pullout even during vibration or pressure spikes.
Below is a practical comparison table of popular mender types:
| Hose Mender Type | Suitable Application |
| Brass Double-Barb Mender | Water, compressed air, general oils |
| SS304 Barb Union Fitting | General industrial fluids, food machines |
| SS316 / SS316L Mender Hose | Sea water, chemical liquids, corrosive gas |
| Heavy-Barb Repair Fitting | High-pressure and high-vibration systems |
(Source: Industry standard design references)
For PU or nylon pneumatic tubing, a barb-style connector is not always ideal.
In those cases, a PU Union Straight Push-In Tube Fitting offers faster installation and a more airtight connection.
Material selection is not only about cost—it directly affects durability, chemical resistance, and long-term sealing reliability. Choosing correctly prevents repeated maintenance and reduces leakage risks.
Brass is widely used for air, water, and light oil systems. It provides stable performance, easy machinability, and excellent sealing with hose clamps.
Distributors prefer brass products because they offer high demand and steady turnover.
SS304 works well with industrial cooling water, mild chemicals, food-grade processes, and environments requiring higher cleanliness. It provides better corrosion resistance than brass without significantly increasing cost.
These materials contain molybdenum, enhancing resistance to chloride ions and aggressive chemicals. SS316/316L is recommended for:
• Sea water applications
• High-corrosion chemical fluids
• Outdoor equipment exposed to salt spray
316L contains lower carbon, making it suitable for hygienic systems and welded pipelines.
Below is a quick selection reference:
| Operating Medium | Recommended Material |
| Compressed air, clean water | Brass / SS304 |
| Lubricants, hydraulic oils | Brass / SS304 |
| Sea water, brine | SS316 / SS316L |
| Weak acids / alkalis | SS316 / SS316L |
| Food and beverage systems | SS304 / SS316L |
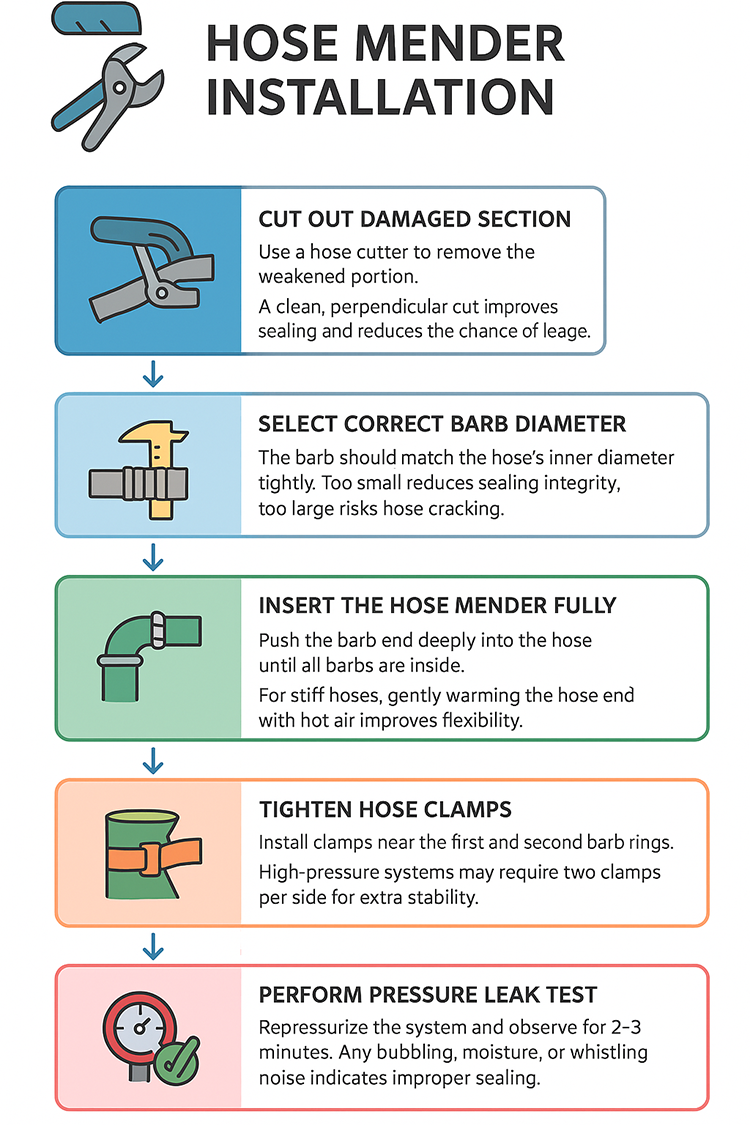
Proper installation ensures long-term sealing, especially when handling air pressure or water flow. The steps below apply to most hoses and union fittings.
PU tubes are commonly used in pneumatic systems powering cylinders, valves, and automation equipment. Their harder wall structure makes them less compatible with barb-type hose menders.
For these applications, a PU Union Straight Push-In Tube Fitting is a better choice.
Its advantages include:
• No hose clamps required
• Fast plug-and-release operation
• Built-in sealing mechanism for airtight performance
• Ideal for systems requiring frequent disconnection
Many automation engineers choose push-in fittings for their compact design and clean installation.
They are also easier for distributors to stock and sell because sizing standards are highly uniform.
FOKCA PU Union Straight Push-In Tube Fittings provide an effortless way to reconnect cut PU hoses and restore airflow within seconds.
These fittings are engineered specifically for PU tubing, nylon tubing, and other plastic air hoses, offering a more efficient repair method compared to traditional barb-and-clamp menders.
With an integrated sealing structure and push-in design, they deliver a tight, leak-free connection that keeps machines running reliably.
 M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
 Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
 Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
 PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
 Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
You May Interest In

Dec 05, 2025 Blog
How to Repair a Damaged Hose Using a Hose Mender





Nov 27, 2025 Blog
Why PVC Pipe Is Flame-Retardant
Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap