Dec 25, 2025
Polyethylene tubing is one of the most widely used plastic tubing types in industrial, pneumatic, water, and general fluid-handling systems. From 1/4 PE tubing in automation equipment to 1 inch polyethylene tubing for water distribution, PE appears everywhere. Yet many buyers and even engineers treat all PE tubing as the same product.
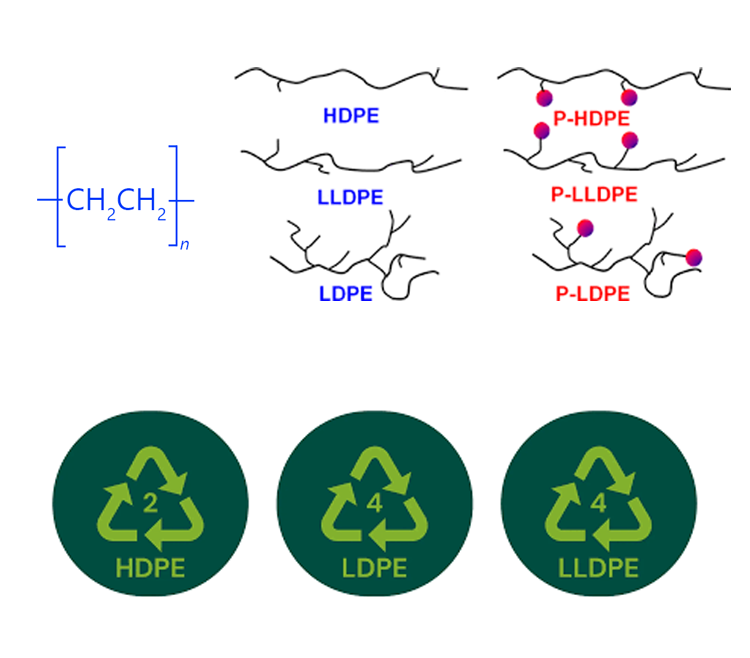
In reality, PE Polyethylene tube performance depends heavily on molecular structure. LDPE, LLDPE, and HDPE share the same base polymer but behave very differently in pressure resistance, flexibility, chemical compatibility, and service life. Choosing the wrong type often leads to premature failure, deformation, or unnecessary cost.
Understanding these differences helps distributors recommend correctly, engineers design reliably, and procurement teams avoid costly misapplications.
The term PE tubing meaning refers broadly to tubing made from polyethylene, a thermoplastic polymer derived from ethylene monomers. However, polyethylene is not a single material. Its properties change significantly depending on molecular chain length and branching density.
In tubing applications, PE is commonly divided into three categories:
1.LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
2.LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene)
3.HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
Each type offers a different balance between flexibility, pressure rating, chemical resistance, and rigidity, which directly impacts how and where it should be used.
LDPE tubing has a highly branched molecular structure, resulting in excellent softness and flexibility. This makes it easy to route, coil, and install, especially in tight spaces or low-stress systems.
LDPE is commonly used for low-pressure fluid transfer, laboratory lines, and consumer products such as squeeze bottles or irrigation drip lines. Many clear or semi-transparent polyethylene tubing products are made from LDPE.
However, its flexibility comes at a cost. Pressure rating is relatively low, and the tubing is more prone to deformation under sustained load or elevated temperature.
Typical LDPE applications include light-duty pneumatic signal lines, gravity-fed water systems, and general-purpose fluid transport.

LLDPE sits between LDPE and HDPE, both structurally and performance-wise. Its linear molecular chains with short branches provide better tensile strength while maintaining reasonable flexibility.
In many industrial environments, LLDPE PE tubing is preferred because it offers:
1.Higher pressure rating than LDPE
2.Better stress crack resistance
3.Improved durability in dynamic applications
This makes LLDPE suitable for polyethylene tubing fittings used in pneumatic control systems, chemical transfer, and medium-pressure water lines. Sizes like pe tubing 3/4, 3/8 pe tubing, and 6mm PE tubing are commonly produced using LLDPE formulations.
For distributors, LLDPE often represents the best all-around recommendation when application details are not extreme in either direction.
HDPE features long, tightly packed molecular chains, resulting in high density and minimal flexibility. Compared with LDPE and LLDPE, HDPE tubing offers significantly higher pressure ratings and excellent long-term dimensional stability.
This is why polyethylene tubing 1 inch, CTS PE tubing, and water distribution lines are typically made from HDPE. It is also widely recognized as polyethylene tubing safe for drinking water, meeting multiple international potable water standards when properly formulated.
The trade-off is rigidity. HDPE is harder to bend and requires careful routing or fittings, especially in compact equipment layouts.
Property | LDPE Tubing | LLDPE Tubing | HDPE Tubing |
Flexibility | Very high | High | Low |
Pressure rating | Low | Medium | High |
Chemical resistance | Good | Very good | Excellent |
Stress crack resistance | Moderate | High | High |
Typical sizes | 1/4, 3/8 | 1/4–3/4 | 1/2–1 inch |
Common uses | Light-duty, labs | Industrial pneumatics | Water, infrastructure |
This comparison explains why PE tubing pressure rating varies widely even for the same outer diameter.
A frequent comparison is polyethylene tubing vs vinyl (PVC). Vinyl tubing is softer and often cheaper, but it relies on plasticizers that can migrate over time, leading to hardening and contamination.
PE tubing, by contrast, is plasticizer-free, offering:
◆Better long-term chemical stability
◆Improved compatibility with food and drinking water
◆Lower risk of material embrittlement
For applications involving drinking water, chemicals, or compressed air, PE tubing is generally the safer and more durable choice.
One of the strongest advantages of PE tubing is its broad chemical compatibility. PE resists many acids, alkalis, alcohols, and neutral fluids, making it suitable for industrial and laboratory environments.
However, aromatic hydrocarbons, strong oxidizers, and certain solvents may require verification. Engineers evaluating pe tubing chemical compatibility should always cross-check the specific PE grade, as LDPE and HDPE behave differently under chemical stress.
Manufacturers like FOKCA Automation provide compatibility guidance based on real application data rather than generic charts, reducing risk in OEM projects.
Understanding everyday examples helps clarify material differences:
◆LDPE: Plastic bags, squeeze bottles, low-pressure tubing
◆LLDPE: Stretch films, industrial hoses, pneumatic tubing
◆HDPE: Water pipes, fuel containers, chemical drums
These familiar products highlight why material choice directly affects performance expectations.
As a global pneumatic component supplier, FOKCA Automation provides a full range of PE Polyethylene tubing, covering LDPE, LLDPE, and HDPE variants. Beyond standard sizes like 1/4 PE tubing or pe tubing 1/2, FOKCA supports OEM/ODM customization based on pressure, flexibility, and regulatory requirements.
For distributors, this means fewer returns and clearer recommendations. For equipment engineers, it means tubing that behaves predictably throughout the machine lifecycle.
Rather than treating PE tubing as a commodity, FOKCA focuses on application-matched solutions, helping customers choose the right material—not just the right diameter.
(FK9026)
 M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
 Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
 Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
 PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
 Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
You May Interest In




Dec 23, 2025 Blog
How to install compression fitting on copper pipe










Dec 08, 2025 Blog
PU Braided Hose for High-Pressure Pneumatic Systems
Dec 05, 2025 Blog
How to Repair a Damaged Hose Using a Hose Mender





Sep 24, 2025 Blog
Can polyurethane tubing be used for fuel lines?

Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap