Nov 26, 2025
In the pneumatic industry, choosing the correct thread type of Pneumatic Quick Couplings is just as important as selecting the right pressure range, flow capacity, or tube size.
Whether you work with Quick Connect Fittings, pneumatic push-in fittings, air valves, pressure regulators, or pneumatic actuators, identifying the right thread standard prevents leakage, improves system reliability,
and ensures your equipment complies with regional and industrial norms.
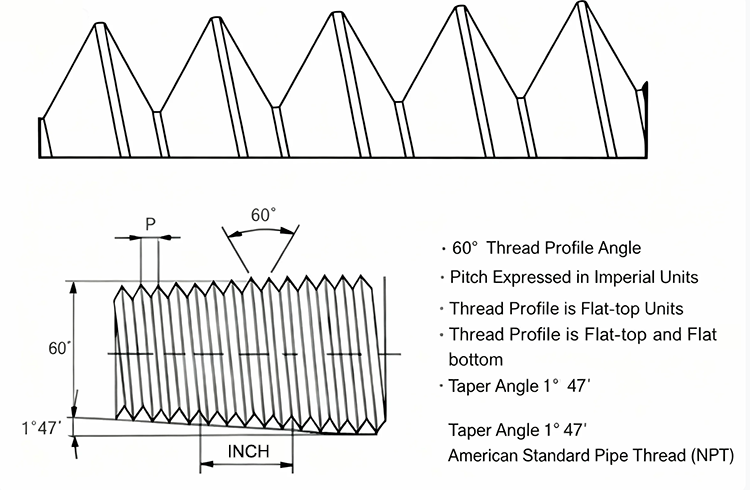
The three most common thread types G, PT, and NPT, they look surprisingly similar.
Yet internally, they differ in sealing mechanisms, thread angles, dimensional standards, and geographic usage.
This guide will help you quickly and accurately distinguish G, PT, and NPT threads, practical advice based on real-world pneumatic system experience.
In pneumatics, even a small mistake in thread selection can lead to:
1.Air leakage and unstable pressure
2.Thread galling, cross-threading, or permanent port damage
3.System shutdowns or maintenance delays
4.Incompatibility between imported equipment and local fittings
Different thread types seem interchangeable, but they never should be mixed. A PT male fitting may appear to screw into an NPT female port,
but the sealing angle mismatch will cause micro-leaks, unsafe pressure drop, or even catastrophic thread failure.
As pneumatic systems become more global, correct thread recognition is not only a technical requirement—it’s a cost-saving measure and a safety guarantee.

Below is a professional yet simple explanation of the three most commonly encountered thread standards.
G Thread (BSPP – British Standard Pipe Parallel)
Key Characteristics:
Parallel threads (constant diameter)
Sealing is achieved using an O-ring or gasket
55° thread angle
Conforms to ISO 228 / BSPP
Popular in Europe, Asia, and widely used in industrial pneumatics
Common Applications:
European pneumatic valves
FRLs (filters, regulators, lubricators)
pneumatic fittings with O-ring face seals
PT Thread (BSPT – British Standard Pipe Taper)
Key Characteristics:
Tapered threads (diameter reduces toward tip)
55° thread angle
Requires thread sealant (PTFE tape)
Popular in Japan, Korea, Taiwan
Also known as JIS standard R/Rc threads
Common Applications:
Japanese pneumatic valves
Asian models of Quick Connect Fittings
Low-pressure piping in APAC industries
NPT Thread (National Pipe Taper – USA Standard)
Key Characteristics:
Tapered threads
60° thread angle (sharper than PT)
Requires thread sealant
Conforms to ANSI/ASME B1.20.1
Mainly used in North America
Common Applications:
U.S. pneumatic solenoid valves
Sensor and manifold ports
North-American pneumatic push-in fittings
If you don't have measuring tools, you can still distinguish the thread type using fast visual cues.
Step 1 — Look for Taper
Hold the fitting at eye level:
No taper → G Thread
Visible taper → PT or NPT
This is the fastest and most reliable first step.
Step 2 — Identify the Sealing Surface
G Thread:
Has a flat sealing face
Usually includes an O-ring
Parallel threads indicate that sealing cannot happen through the thread
PT / NPT:
No flat face
Seals by metal-to-metal thread wedging
Must use thread seal tape
Step 3 — “Tooth Sharpness” Test
Run your nail gently across the thread:
NPT feels sharper (due to its 60° angle)
PT feels smoother/rounder
G feels uniform along the length
This technique is widely used by technicians in the field.
When precision is required—especially for OEM production, engineering design, or QC inspection—use proper thread measurement tools.
Thread Gauge (Pitch Gauge)
55° gauge for G / PT
60° gauge for NPT
Ensures exact matching of pitch and angle
Even slight mismatch will indicate a wrong thread.
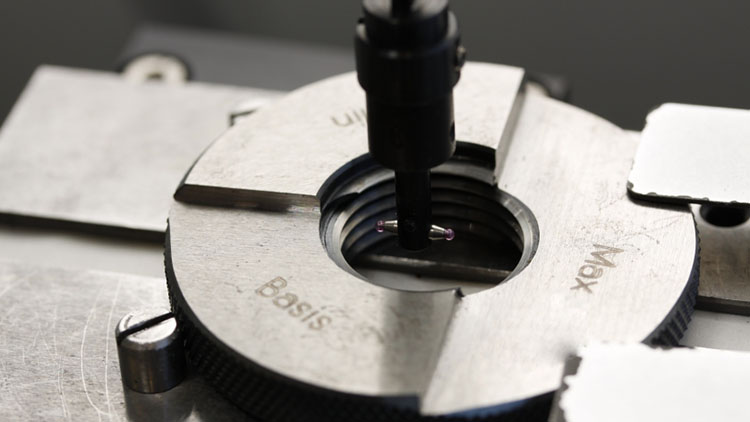
Caliper Measurement – Outside Diameter
Typical example for 1/4 size:
G1/4 → ~13.1 mm
PT1/4 → ~13.2 mm
NPT1/4 → ~13.7 mm
These small differences matter when sealing under pressure.
When you have a G-type female-thread fitting on hand, you can match it with a male-thread fitting by tightening them together.
If they fit perfectly without gaps or resistance, the male-thread fitting is also a G-type fitting. The same principle applies in reverse.
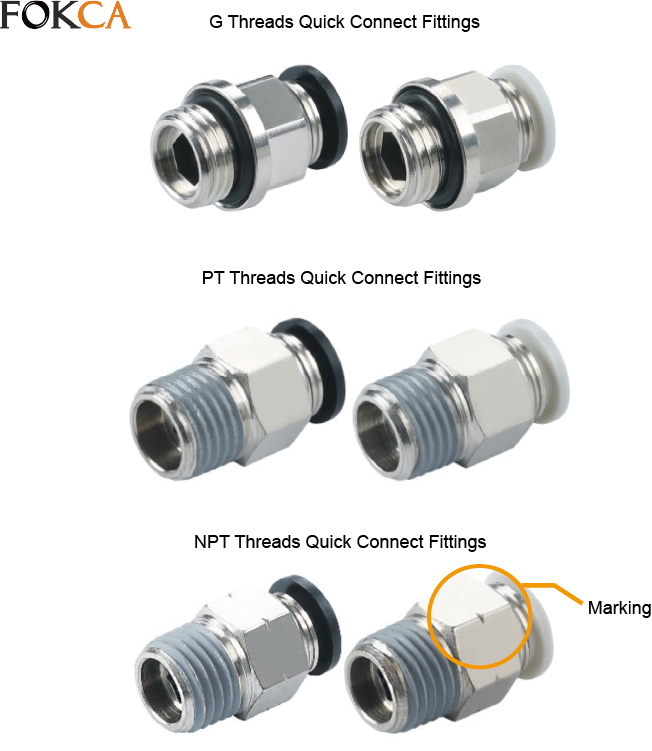
To help users quickly and conveniently distinguish between PT and NPT threaded pneumatic push-in fittings, many manufacturers apply specific markings to their products.
FOKCA follows the same principle. On our fittings, NPT threads are engraved with a groove mark, allowing customers to instantly identify the thread type upon receiving the goods.
This greatly improves accuracy and efficiency during installation.
If you are looking for such products or need reliable thread-standard solutions, feel free to contact us—FOKCA is ready to support you.

| Thread Type | Recommended Applications | Typical Usage Scenarios | Main Advantages |
| G Thread (BSPP) | FRL units (filter, regulator, lubricator) Directional valves | European-made equipment | Zero leakage with O-ring sealing, easy installation, ideal for panel-mounted equipment |
| PT Thread (BSPT) | Japanese pneumatic system Maintenance systemss | Compact Asian machinery Environments where PTFE tape is standard | Reliable in small-diameter fittings and high-vibration environments |
| NPT Thread | North American industrial system U.S.-standard Quick Connect Fittingss | Compressed air automation lines High-pressure and cycling systems | Tight mechanical seal from 60° taper ensures stability in pressure cycles |
Choose the Right Thread, Protect Your Pneumatic System
Correctly identifying G, PT, and NPT threads ensures:
leak-free operation
long-term durability
safer pneumatic systems
lower maintenance cost
compatible global installations
Whether you're specifying components, maintaining an air system, or sourcing pneumatic push-in fittings, Quick Connect Fittings, or pneumatic fittings, thread awareness is essential.
If you need:
-High-quality pneumatic fittings in all thread standards
-OEM customization and private-label manufacturing
-Technical consultation on G / PT / NPT compatibility
I can help you choose the most suitable products for your application.
If you would like to learn more about pneumatic push-in fittings, pneumatic tubing, or other air-line components, please feel free to contact us at any time.
FOKCA is committed to providing you with the most professional support and service.

(FK9026)
 M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
M5 and 4mm Selection Logic for Mini Type Pneumatic Push In Fittings in Micro Equipment
 Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
Polyurethane Tube Hardness and Its Influence on Pneumatic System Response Speed
 Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
Drag Chain Polyurethane Tube: Why 95A and 98A PU Tubing Perform Better in Automation Systems
 PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
PVC Flexible Tubing in Vacuum Systems: Preventing Collapse and Flow Loss
 Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
Nylon Tubing Materials: Is PA66 Stronger Than PA6
You May Interest In




Dec 04, 2024 Blog
Application Of Tube FittingLinks: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap