Feb 03, 2026
In pneumatic systems, a Hand Valve is often considered a simple manual control component. However, incorrect installation direction is a surprisingly common cause of system malfunction. When the valve body orientation or inlet and outlet markings are ignored, even a well-designed circuit can suffer from unstable control, unexpected leakage, or safety risks.
Understanding how a hand valve pneumatic should be used during installation helps engineers avoid basic mistakes that later become costly troubleshooting issues.
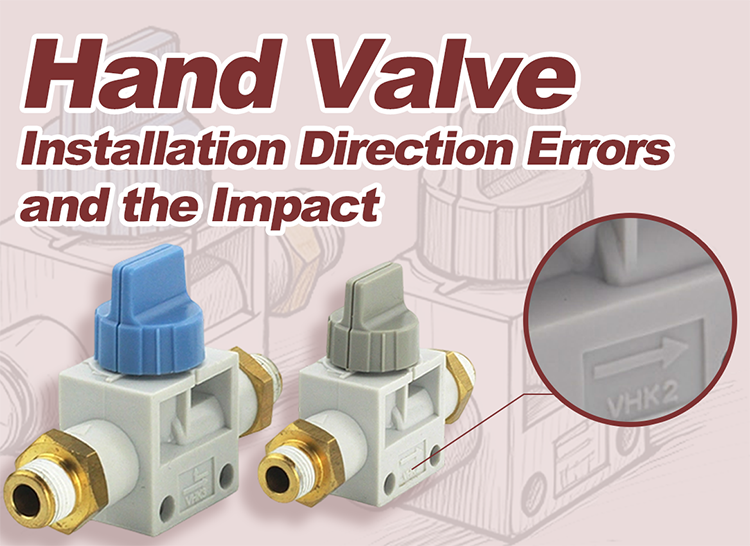
Most Pneumatic Push-in Manual Valve designs are directional. Internal seals, valve spools, and exhaust paths are optimized for a specific flow direction. When the inlet and outlet are reversed, airflow no longer follows the intended path.
This can result in delayed pressure build-up or incomplete exhaust. In manual control stations, operators may feel that the valve response is “soft” or inconsistent.
In reality, the issue is not the valve quality but the installation direction.
A frequent problem on factory floors is overlooking port markings during installation. In compact equipment or retrofit projects, installers may rely on hose routing convenience instead of valve labeling.
When a hand valve pneumatic is installed backward:
◆Internal seals may be pressurized from the wrong side
◆Exhaust ports may be partially blocked
◆Minor internal leakage becomes continuous leakage
Over time, this leads to air loss and unstable downstream pressure, especially in manual start or emergency stop circuits.

Incorrect orientation does not always cause immediate failure. Instead, it creates subtle control anomalies. For example, cylinders may extend normally but retract slowly, or pressure may not fully release after manual shut-off.
In safety-related circuits, this is particularly dangerous. A Hand Valve that cannot fully exhaust air compromises operator safety, as residual pressure remains in actuators. For engineers accustomed to hand valve SMC layouts, these symptoms often indicate reversed installation rather than component defects.
Another overlooked consequence is accelerated seal wear. When pressure loads act on valve seals in unintended directions, friction and deformation increase.
This leads to:
1.Premature seal aging
2.Gradual increase in internal leakage
3.Shortened service life of the Hand Valve
From a maintenance perspective, the valve appears to “fail early,” while the true cause lies in incorrect installation rather than material quality.
Clear identification of flow direction significantly reduces installation errors. Valves with visible arrows, port labels, or body engravings help installers verify orientation at a glance.
| Feature | Poorly Marked Hand Valve | Clearly Marked Hand Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Flow direction visibility | Low | High |
| Installation error risk | High | Low |
| Troubleshooting time | Longer | Shorter |
| Suitability for OEM assembly | Limited | Preferred |
For distributors and OEM builders, clear marking directly translates into fewer after-sales issues.
To avoid direction-related problems, engineers should follow a few practical steps:
◆Always verify inlet and outlet markings before connecting hoses
◆Match valve orientation with pneumatic schematics
◆Perform a low-pressure functional test after installation
A correctly installed Hand Valve ensures predictable control and full exhaust, which is critical for both performance and safety.
When selecting a Pneumatic Push-to-Connect Manual Valve for automation equipment, clarity of design should be a key criterion. Beyond pressure rating and port size, consider:
◆Visibility of directional arrows
◆Consistency of marking across product series
◆Compatibility with existing hand valve SMC layouts
Valves designed with intuitive markings reduce training costs, speed up assembly, and minimize installation-related failures in the field.
For systems where manual control reliability is critical, choosing a clearly marked Hand Valve is not a cosmetic preference but a functional necessity.
(FK9026)
 Carbon Steel Connector Load Capacity Advantages in High-Pressure Pneumatic Systems
Carbon Steel Connector Load Capacity Advantages in High-Pressure Pneumatic Systems
 Hand Valve Installation Direction Errors and Their Impact on Pneumatic Systems
Hand Valve Installation Direction Errors and Their Impact on Pneumatic Systems
 Why Some Hydraulic Quick Coupling Allow More Air Inclusion
Why Some Hydraulic Quick Coupling Allow More Air Inclusion
 How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Quick Coupler: Types, Features, and Applications
How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Quick Coupler: Types, Features, and Applications
 Why High-Precision Vacuum Filters Are Better for the Electronics Industry
Why High-Precision Vacuum Filters Are Better for the Electronics Industry
You May Interest In








Jan 19, 2026 Blog
Signs It’s Time to Replace Your Pneumatic Nylon Tube




Jan 06, 2026 Blog
How to Measure NPT Threads Accurately on a Fitting
Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap