Jul 25, 2025
Polyolefin, as a common raw material for heat-shrink tubing, may seem entirely unrelated to flame retardancy—after all, conventional wisdom holds that such hydrocarbon polymers are inherently combustible. However, advancements in modern materials science have successfully unified these seemingly contradictory properties of "heat-shrinkability" and "flame retardancy" in polyolefin tubing, achieving perfect harmony.
Through electron beam or gamma radiation cross-linking technology, polyethylene/polypropylene molecular chains form a three-dimensional network structure. This not only endows the material with a "memory effect" (heat-shrink characteristic) but also significantly enhances its temperature resistance (up to 125°C or higher). The flame retardant properties are achieved through the following core technologies:
Halogen-free flame retardant systems
Nano-modification technology
Synergistic formulation design
Temperature Range Related to Heat-Shrink Performance
Shrink initiation temperature: ≥70°C
Complete shrinkage temperature: 120°C~135°C
Long-term operating temperature:
Standard type: -55°C ~ 105°C
High-temperature modified type: -60°C ~ 125°C
Note:
Below -55°C, the material may harden and lose flexibility.
Prolonged exposure to temperatures above the upper limit will accelerate aging.
Effective flame retardant temperature range:
Within -40°C ~ 125°C, flame retardants remain stable, ensuring UL94 V-0 self-extinguishing performance.
Above 125°C, some flame retardants may decompose and fail.
Flammability testing standards:
o UL94 V-0 requires self-extinguishing within 2 seconds after flame removal at 23°C±2°C.
o High-temperature environments (e.g., 100°C) require post-thermal-aging flame retardant testing.
Flame-Retardant Polyolefin heat-shrink tubing achieves exceptional performance through innovative material design, successfully combining the superior properties of thermoplastic polyolefins with high-efficiency flame-retardant characteristics.
Lightweight & Flexible: Low density with a small bending radius, enabling easy installation in complex wiring layouts.
Chemical Resistance: Resistant to acids, alkalis, and oils (e.g., automotive transmission fluid), outperforming standard PVC materials.
Electrical Insulation: Dielectric strength >20 kV/mm, making it ideal for high-voltage cable insulation.
Intelligent Memory Effect: Shrinks uniformly at 120°C~135°C, forming a tight seal around cables without compromising flame-retardant additives.
Process Compatibility: Compatible with heat guns, ovens, or infrared heating for quick installation, with no degradation in flame-retardant performance.
• Automotive Industry: High-voltage wiring harness protection.
• Electronic Devices: Insulation sleeves for lithium battery packs.
• Industrial Sector: Mining cable protection.
• Rail Transportation: In-cabin cable management
PVC Heat Shrink Tubing
• Base Material Properties: PVC inherently contains chlorine (Cl), providing natural flame retardancy as it releases hydrogen chloride (HCl) during combustion to suppress flame spread.
• Additive Enhancement: Typically supplemented with flame retardants to further improve fire resistance ratings.
• Self-Extinguishing: Complies with UL94 V-0/V-1 standards, extinguishing rapidly after flame removal.
Polyolefin Heat Shrink Tubing
• Base Material Properties: Polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP) are inherently flammable, producing molten drips that may propagate flames.
• Dependence on Flame Retardants: Requires significant flame-retardant additives (e.g., aluminum hydroxide, brominated compounds) to achieve fire resistance.
• Modification Technology: Advanced polyolefin tubing employs cross-linking modification combined with flame-retardant composites to meet UL94 V-0 standards.

Application Scenario Recommendations
Choose PVC Heat Shrink Tubing if:
◆ Cost-effective flame retardant solution required
◆ Halogen restrictions are not stringent.
◆ Fast self-extinguishing properties needed.
Choose Polyolefin Heat Shrink Tubing if:
◆ Halogen-free eco-friendly material required.
◆ Higher operating temperatures expected.
◆ Superior chemical resistance and flexibility needed.
Selection Recommendations:
Verify Manufacturer Case Studies: Request successful application examples in similar industries.
Small-Batch Trial Production: Test shrinkage rate and aging performance.
Supply Chain Stability: Ensure reliable raw material sources to avoid price fluctuations affecting delivery.
In summary, only cross-linked polyolefin materials possess heat shrinkability. Heat shrink tubing is widely used, offering numerous advantages and coming in various types, including PP, LDPE, and LLDPE. Contact us directly for the latest product pricing and our full product catalog.
 PUAS Polyurethane Tubing: Flexible, Durable, and Anti-Static Solution for Industrial Applications
PUAS Polyurethane Tubing: Flexible, Durable, and Anti-Static Solution for Industrial Applications
 Which Pneumatic Fittings Perform Best in High-Vibration Applications
Which Pneumatic Fittings Perform Best in High-Vibration Applications
 Why Pneumatic Tubing Should Not Be Bent Immediately After an SMC One Touch Fitting
Why Pneumatic Tubing Should Not Be Bent Immediately After an SMC One Touch Fitting
 Why Aluminum Foil Is Added to PUFR Flame-Resistant Hose and How It Improves Fire Performance
Why Aluminum Foil Is Added to PUFR Flame-Resistant Hose and How It Improves Fire Performance
 Why Nylon Hose Leaks: The Real Causes Behind Air Loss at Fittings
Why Nylon Hose Leaks: The Real Causes Behind Air Loss at Fittings
You May Interest In

May 07, 2025 Blog
Comprehensive Analysis of Pneumatic Push in Fittings
Apr 22, 2025 Blog
Solution for Nylon Tube
Apr 16, 2025 Blog
PVC Tubing vs. Polyurethane Tubing
Apr 10, 2025 Blog
What is the difference between pu and pvc
Feb 24, 2025 Blog
How to Identify Hydraulic Quick Couplers?
Jan 21, 2025 Blog
How to Measure Pipe Thread?
Jan 16, 2025 Blog
What Is Pipe thread?
Dec 04, 2024 Blog
Application Of Tube Fitting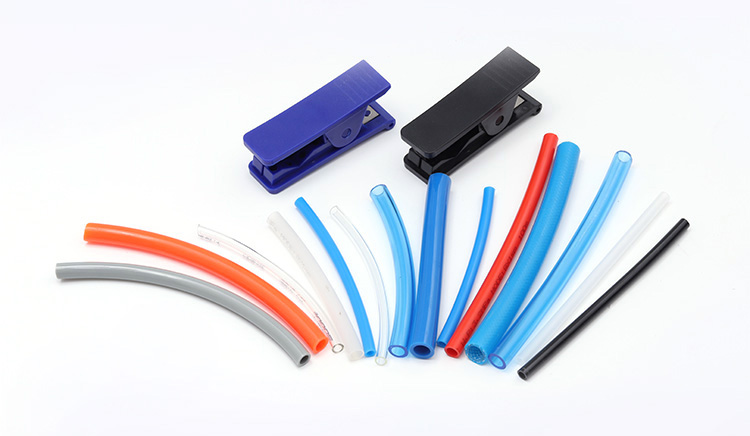

Jun 26, 2023 Blog
What Is The Difference Between LLDPE And LDPE?
Jan 17, 2023 Blog
What Are The Classification Of Plastics?Links: www.fescolo.com(Pneumatic)
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap